───✱*.。:。✱*.:。✧*.。✰*.:。✧*.。:。*.。✱ ───
Part 1
Largest Memory
- What is the largest memory that can have a starting or lowest address of
- → 24 bit number (21 without leading zeroes)
- Max address space →
- Remaining space →
High and Low Addresses
- What are the high and low addresses of the memory ranges defined by the chip select shown?
- 5-input active low NAND, where , , and are inverted
- (direct input)
- (inverted)
- (inverted)
- (direct input)
- (inverted)
- to (5 bits) are chip select, to (23 bits) are unimportant
- Low address →
- High address →
- 5-input active low NAND, where , , and are inverted
Processor Memory Space
- What is the processor memory space for the chip in problem 2?
- to is 28 bits
Memory Device Size
- What is the memory device size for each chip select in problem 2?
Devices in Processor
- How many 16K memories can be placed (without overlapping) in the memory space of a processor that has 24 address lines?
- Processor memory space →
- Each device →
- Total devices →
Active Low Chip Select
- Using logic gates, design an active low chip select for each of the following situations
- A 256K memory device starting at address in a 4 meg memory space
- Address range
- Low →
- High →
- Bit pattern → , Variables →
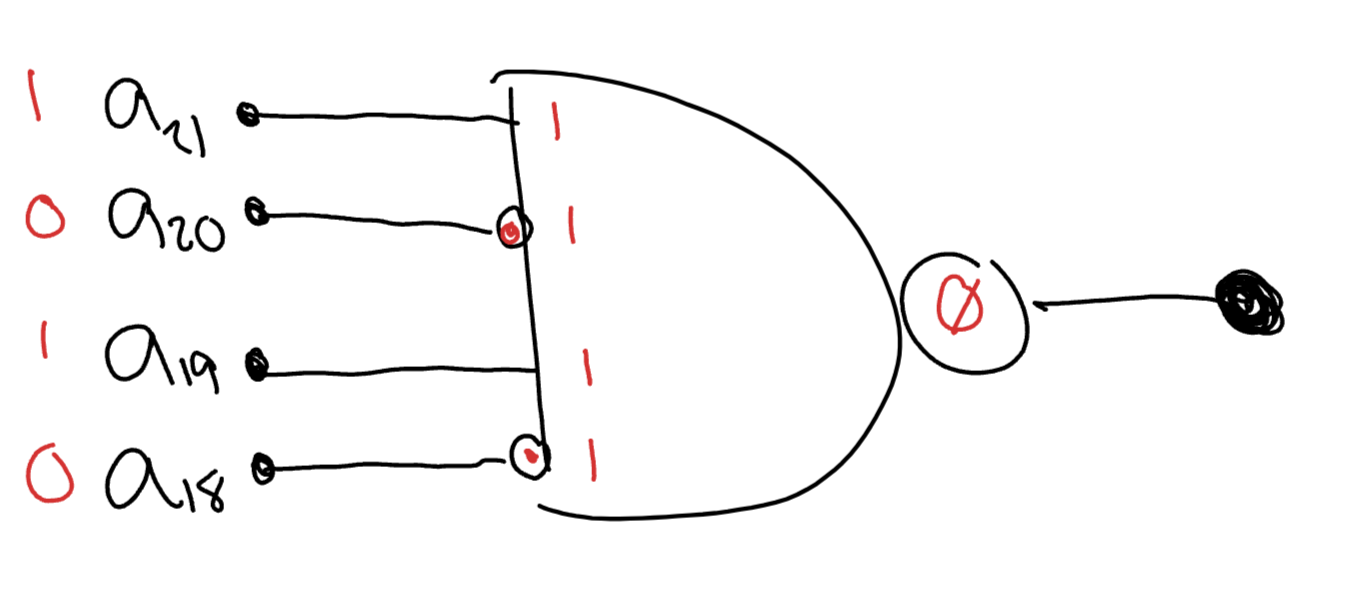
- Address range
- A memory device in the range to in a 1 meg memory space
- address lines
- Low →
- High →
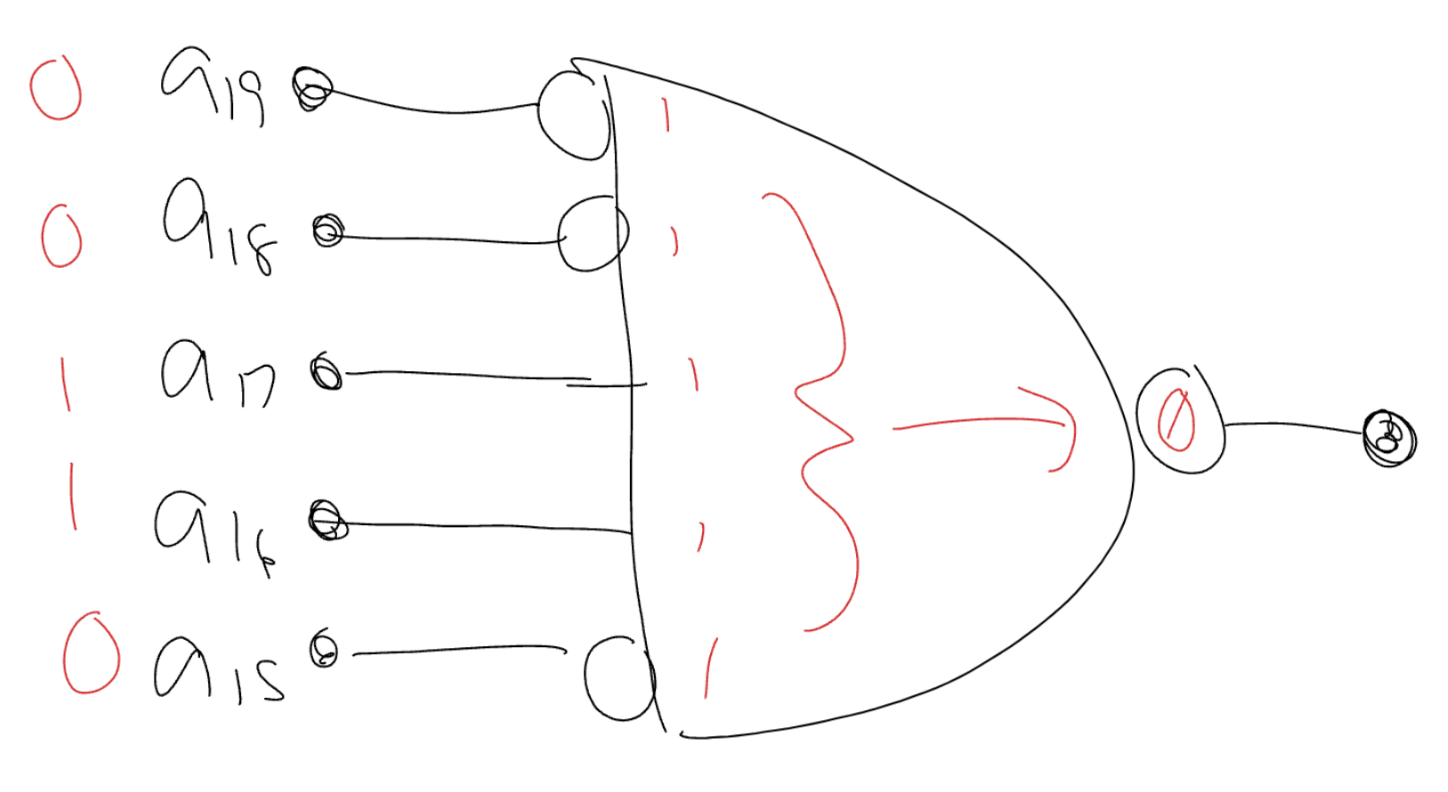
- A 256K memory device starting at address in a 4 meg memory space
SRAM & DRAM
- How many latches are contained in a SRAM that has 20 address lines and 8 data lines
- Address lines →
- Data lines → 8
- Latches →
- True or false: DRAM is faster than SRAM. Why?
- False, DRAM has less components and has changing data
- True or false: DRAM is cheaper per bit than SRAM. Why?
- True, DRAM (1 transistor + 1 capacitor per bit), SRAM (6 transistors per bit)
- True or false: More DRAM can be packed into the same area than SRAM. Why?
- True, less components take up less space
- Which is usually used for smaller memories, DRAM or SRAM? Why?
- SRAM, speed
Data Signals
- When data is passed from a memory chip to the processor, what values do the bus signals and have?
Class C IPv4
- What is the subnet and host id of the Class C IPv4 address ?
- Class C →
- Subnet →
- Host ID →
- Taking into account the address for the subnet and broadcast, how many hosts can be present on a Class C IPv4 subnet? Why?
- Class C has 8 host bits → addresses
- The network and broadcast addresses can’t be used → only addresses are available.
Control Lines
- A processor uses separate control lines for memory and I/O operations. For each of the scenarios below, determine the values of
- The processor needs to read data from RAM at address
- The processor wants to send a command byte to a printer
- The processor is checking the status of a keyboard
- The processor is storing a variable to main memory
- The processor needs to read data from RAM at address
- What happens if = 0 and = 0 simultaneously? Why is this a problem?
- Signal conflict → data damage.
Part 2
Registers
- List the types of registers utilized by the processor an describe their operation.
- General purpose (accumulators) → stores data for arithmetic/logic
- Address (pointer) → address to variable in memory
- Index → string/array processing
- Stack pointer → points to the top of the stack in memory
- Instruction pointer → address of the next instruction to be executed
- Determine the settings of the zero flag, the carry flag, and the sign flag for each of the following 8-bit operations
- If registers A, B, and C contain the values 12, 65, and 87 respectively, and they are pushed into the stack in the order A, then B, then C, what values do A, B, and C have if they are pulled from the stack in the order C, then A, then B?
- Pushed →
- Pull →
Processor Architecture
- List and describe the purpose of each of the components of the processor
- Bus → provides communication pathways for devices
- Register → high-speed storage within processor
- Flag → indicates the result of a processor operation
- Buffer → temporary storage that handles speed difference between components
- Stack → stores data during subroutine calls and interrupts
- I/O Port → interface between processor and I/O devices
- List and describe the purpose of each of the components of the CPU
- ALU (arithmetic logic unit) → does math & logic operations
- CPU Registers → high speed storage accessible by the ALU
- Instruction Decoder → interprets machine code instructions
- Internal Data Bus → provides pathways for data within the CPU
- Control Unit → coordinates and controls CPU operations & send signals
- What type of instruction might force the processor to flush the pipeline? Why?
- Branch/conditional jump → branching changes the instruction flow
- Exceptions → when an exception occurs, the current execution context might need to be saved (and the pipeline flushed)
───✱*.。:。✱*.:。✧*.。✰*.:。✧*.。:。*.。✱ ───